Appearance
https://juejin.cn/post/6844904046436843527#heading-19
获取数组的最后一个元素: at(-1)
数组与对象的相互转换
对象到数组: Object.entries() 数组到对象: Object.fromEntries()本地文件预览
createObjectUrl
文件秒传
服务器已经存有一份了,不需要再次上传。这个文件的文件名由文件内容hash而成。
需要服务器提供一个接口,返回已经上传的分片和大小。
切片上传
1.获取arrayBuffer : blob.arrayBuffer() 或者 fileReader.readAsArrayBuffer()
利用浏览器提供的web cryptography api, 它用于计算传入数据的sha-256 算法。
2.计算哈希:await crypto.subtle.digest('SHA-256',arrayBuffer)
计算文件内容的hash会很慢,可以用worker,防止耗时操作阻塞UI线程
3.得到文件名之后,就可以处理切片了
切片数量的动态调整
content-type的application/octet-stream 和 form-data区别
用字节流的话只能上传二进制文件
如果用formData的话可以同时上传文件和普通字段
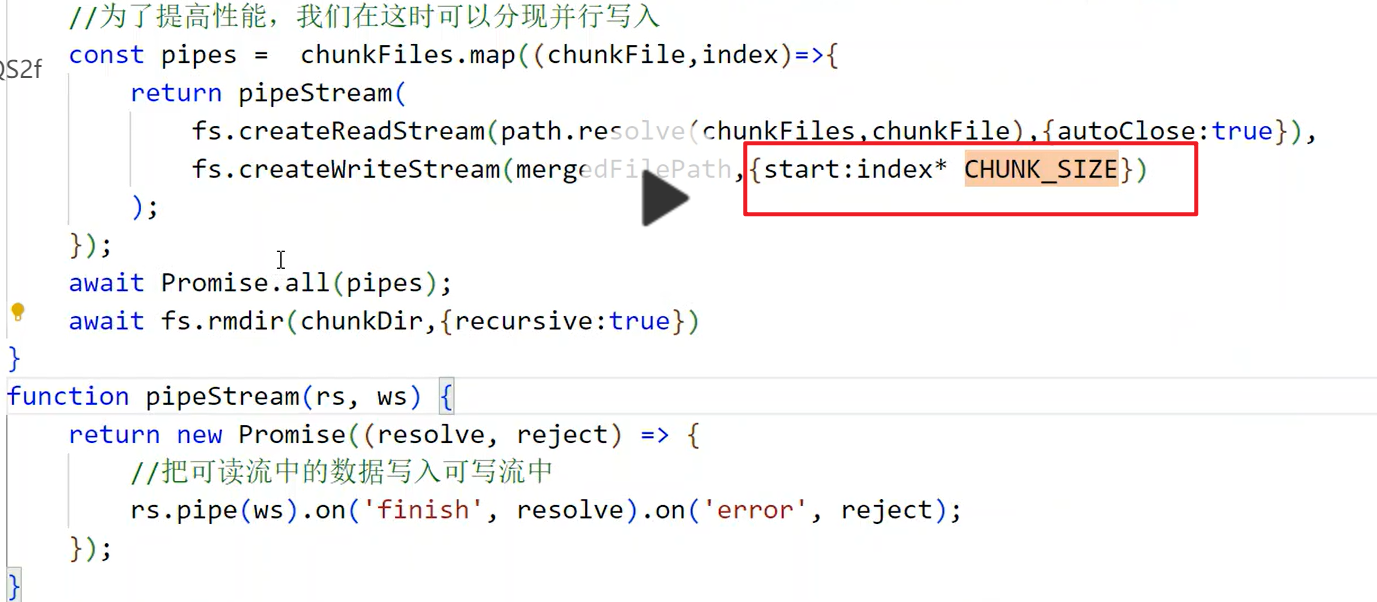
并行写入
利用可写流可以指定写入位置
暂停上传
控制上传的状态:未上传,上传中,已暂停
存放所有上传请求的cancel token
调用cancel方法,axios会抛出错误,在try catch里面用isCancel方法判断是否为用户取消暂停的而导致的异常
恢复上传(即断点续传)
服务端需要提供一个接口,获取每个分片上传了多少,以便客户端上传分片剩下的部分
const remainingChunk = file.slice(uploadedSize)
如果remainingChunk.size==0 则表示已经上传完成,直接resolve即可
断点续传还需要给接口传 分片的起始索引,用于服务端给分片的写入位置
worker
与主线程隔离,有自己的全局上下文,不能访问dom, window
控制并发上传的数量
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>File Upload Demo</title> </head> <body> <input type="file" id="fileInput" /> <button onclick="startUpload()">Start Upload</button> <script> // Mock function to simulate uploading a file chunk function uploadChunk(chunk) { return new Promise(resolve => { // Simulate asynchronous upload setTimeout(() => { console.log(`Uploaded chunk: ${chunk}`); resolve(); }, Math.random() * 1000); // Simulating network latency }); } // Function to handle file upload async function startUpload() { const fileInput = document.getElementById('fileInput'); const file = fileInput.files[0]; const chunkSize = 1024 * 1024; // 1 MB chunk size const totalChunks = Math.ceil(file.size / chunkSize); const concurrencyLimit = 5; // Maximum concurrent uploads let uploadedChunks = 0; async function uploadNextChunk() { if (uploadedChunks >= totalChunks) { console.log('Upload completed'); return; } const start = currentChunk * chunkSize; const end = Math.min((currentChunk + 1) * chunkSize, file.size); const chunk = file.slice(start, end); console.log(`Uploading chunk ${currentChunk + 1}/${totalChunks}`); // Simulate upload and wait for it to complete await uploadChunk(chunk); uploadedChunks++; // Upload the next chunk uploadNextChunk(); } // Start initial uploads (up to the concurrency limit) const initialUploads = Math.min(totalChunks, concurrencyLimit); for (let i = 0; i < initialUploads; i++) { uploadNextChunk(); } } </script> </body> </html>